随着PTE考生对PTE口语和PTE听力的重视,大家口语和听力的分数得到极大提高,但是PTE阅读渐渐成为考生们新的难题。
墨尔本悉尼文波PTE特别为PTE考生们挑选了适合练习PTE阅读的文章,主题,内容,长度都与PTE阅读题中的文章相似。激活学过的词汇,更新新的词汇,提高阅读速度,全面提升自己的阅读能力。
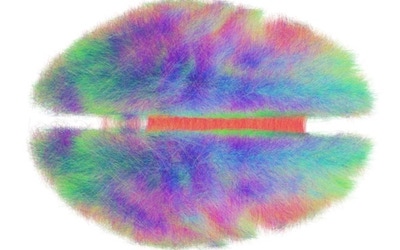
The human brain is an extraordinarily complex network, comprising an estimated 86 billion neurons connected by 100 trillion synapses. A connectome is a comprehensive map of these links—a wiring diagram of the brain.
With current technology, it is not possible to map a network of this size at the level of every neuron and synapse. Instead researchers use techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging to map connections between areas of the human brain that span several millimeters and contain many thousands of neurons.
At this macroscopic scale, each area comprises a specialized population of neurons that work together to perform particular functions that contribute to cognition. For example, different parts of your visual cortex contain cells that process specific types of information, such as the orientation of a line and the direction in which it moves. Separate brain regions process information from your other senses, such as sound, smell and touch, and other areas control your movements, regulate your emotional responses, and so on.
These specialized functions are not processed in isolation but are integrated to provide a unitary and coherent experience of the world. This integration is hypothesized to occur when different populations of cells synchronize their activity. The fiber bundles that connect different parts of the brain—the wires of the connectome—provide the substrate for this communication. These connections ensure that brain activity unfolds through time as a rhythmic symphony rather than a disordered cacophony.
Synapse: n. (神经元轴突的)突触。
Connectome: n.神经连接体。
Magnetic resonance imaging: 磁共振成像。
Visual Cortex:视觉皮质。
Unitary:adj. 单一的,个体的。
Cacophony: n. 刺耳的嘈杂声。
墨尔本悉尼文波PTE原创首发
更多精彩请持续关注微信wenbo_tv2。